Pair-state basis calculations#
Preliminaries#
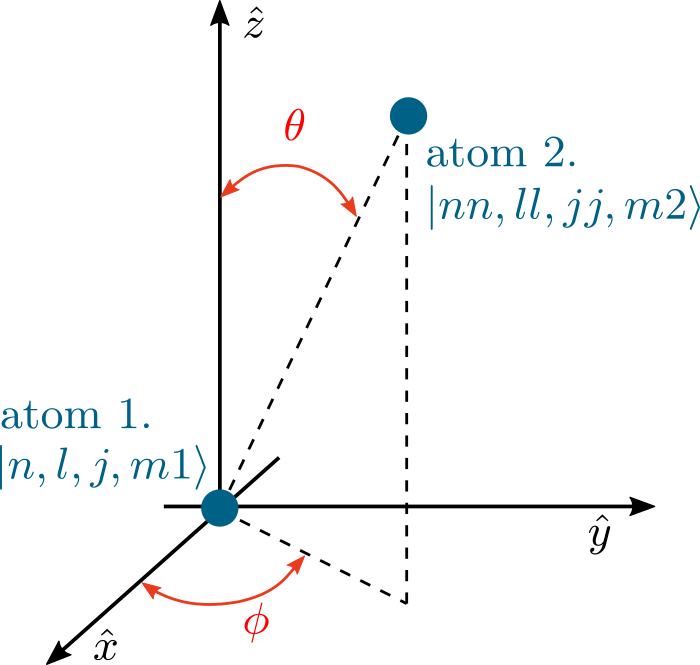
Relative orientation of the two atoms can be described with polar angle \(\theta\) (range \(0-\pi\)) and azimuthal angle \(\phi\) (range \(0-2\pi\)). The \(\hat{z}\) axis is here specified relative to the laser driving. For circularly polarized laser light, this is the direction of laser beam propagation. For linearly polarized light, this is the plane of the electric field polarization, perpendicular to the laser direction.
Internal coupling between the two atoms in \(|n,l,j,m_1\rangle\) and \(|nn,ll,jj,m_2\rangle\) is calculated easily for the two atoms positioned so that \(\theta = 0\), and for other angles wignerD matrices are used to change a basis and perform calculation in the basis where couplings are more clearly seen.